Scanner abdominale et appendagite épiploïque
Salah Ben Elhend, Redouane Roukhsi
Corresponding author: Salah Ben Elhend, Radiology Department, HMA Military Hospital, Marrakech, Morocco 
Received: 26 Dec 2019 - Accepted: 19 Jan 2020 - Published: 22 Jan 2020
Domain: Radiology
Keywords: Appendice épiploïque, inflammation, scanner
©Salah Ben Elhend et al. PAMJ Clinical Medicine (ISSN: 2707-2797). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Salah Ben Elhend et al. Scanner abdominale et appendagite épiploïque. PAMJ Clinical Medicine. 2020;2:17. [doi: 10.11604/pamj-cm.2020.2.17.21404]
Available online at: https://www.clinical-medicine.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/2/17/full
Scanner abdominale et appendagite épiploïque
Abdominal CT scan and epiploic appendagitis
Salah Ben Elhend1,&, Redouane Roukhsi1
1Radiology Department, HMA Military Hospital, Marrakech, Morocco
&Auteur correspondant
Salah Ben Elhend, Radiology Department, HMA Military Hospital, Marrakech, Morocco
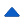
Epiploic appendagitis is subserosal pediculated fat on the external surface of the colon, covered by peritoneum. It is characterized by terminal vascularization. It mainly affects left colon. Appendagitis, or torsion of epiploic fringe, is an isolated inflammation of the epiploic appendix. CT scan usually shows intraperitoneal, often oval, well defined fat mass with a fine edge of increased density on the surface of the colon enhanced after injection of iodinated contrast material (" small ovoid fat mass" with "ring sign").
Key words: Appendix epiploic, inflammation, CT scan
Un appendice épiploïque est une formation graisseuse sous séreuse pédiculée de la surface externe du colon, recouverte de péritoine. La vascularisation est terminale. La localisation préférentielle est le colon gauche . Une appendagite, ou torsion de frange épiploïque, est une inflammation isolée d'un appendice épiploïque. La tomodensitométrie objective une: masse de densité graisseuse intra-péritonéale, accolée au colon, souvent ovale, bien limitée par un fin liseré de densité plus élevée, réhaussé après injection de produit de contraste iodé (« small ovoid fatty mass » avec un « ring sign »).
Figure 1: TDM abdomino-pelvienne en coupe axiale: Masse de densité graisseuse intra péritonéale au contact du muscle droit droit, illustrant un ring sign (flèche blanche)